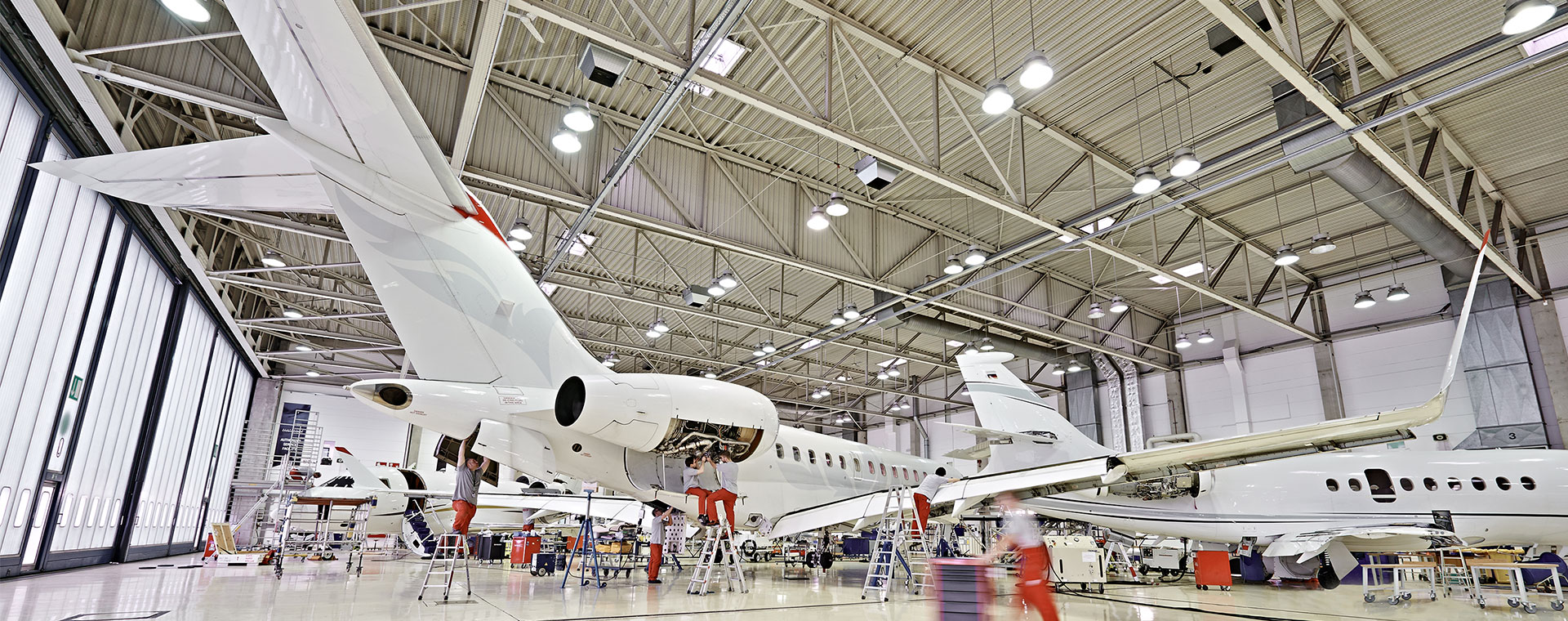
In the fast-paced world of aviation, aircraft servicing plays a vital role in ensuring passenger safety, operational efficiency, and compliance with strict industry regulations. From routine inspections to complex repairs, the process has evolved significantly over the years—driven largely by cutting-edge technology. Today, advancements such as predictive maintenance systems, drone-assisted inspections, and digital record management are transforming how aircraft are maintained. Whether handled by a global airline or a certified aircraft technician Florida, modern servicing techniques are designed to minimize downtime, enhance reliability, and keep flights operating smoothly.
Aircraft Servicing
Aircraft servicing is one of the most crucial aspects of the aviation industry. It is the process that ensures every aircraft—whether a commercial airliner, private jet, or cargo plane—remains airworthy, reliable, and safe for operation. This involves a combination of routine checks, preventive maintenance, repairs, and detailed inspections performed at specific intervals or when needed. Modern servicing doesn’t just involve wrenches and manual inspections—it combines highly skilled technicians, advanced diagnostic tools, and sophisticated technology to keep aircraft performing at peak efficiency.
What is Aircraft Servicing?
Aircraft servicing refers to the range of maintenance activities carried out to ensure the safety, functionality, and performance of an aircraft. These activities include:
Routine Checks
-
Pre-flight Checks – Quick inspections before every flight to ensure all systems are functioning properly.
-
Post-flight Checks – Assessments performed after landing to detect any issues caused during the flight.
-
Transit Checks – Conducted when an aircraft is on the ground between flights, focusing on fluid levels, tire condition, and visible wear.
Scheduled Maintenance
-
A-Checks – Light inspections performed every few hundred flight hours, usually overnight at an airport hangar.
-
C-Checks – More in-depth inspections carried out every 12–18 months, requiring the aircraft to be taken out of service for several days.
-
D-Checks – The most comprehensive overhaul, performed every 6–10 years, involving complete disassembly and inspection of the aircraft.
Repairs and Overhauls
-
Fixing damaged components or replacing worn-out parts.
-
Engine overhauls to restore performance and efficiency.
Specialized Inspections
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) to detect structural cracks without damaging the aircraft.
-
Use of borescopes to inspect internal engine and structural components.
Why is Aircraft Servicing Important?
The importance of aircraft servicing extends far beyond keeping an aircraft “looking good.” It’s directly linked to safety, compliance, and operational performance.
1. Passenger Safety
Aircraft operate under extreme conditions—high altitudes, rapid temperature changes, and constant vibration. Without regular maintenance, even minor defects can escalate into dangerous failures. Servicing ensures that every critical system, from engines to landing gear, operates without risk.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Aviation authorities such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) require airlines and maintenance providers to follow strict maintenance schedules. Failure to comply can lead to severe penalties, grounding of aircraft, or loss of operating licenses.
3. Operational Efficiency
An aircraft that’s well-maintained runs more efficiently, burns less fuel, and experiences fewer delays due to mechanical issues. This not only saves costs for airlines but also improves on-time performance for passengers.
4. Extending Aircraft Lifespan
Routine servicing helps prevent major breakdowns, keeping aircraft in service for decades. Many airliners can operate for 20–30 years if maintained properly.
The Evolution of Technology in Aviation Maintenance
Aircraft maintenance has come a long way since the early days of aviation. Decades ago, inspections and repairs relied heavily on manual labor, physical checklists, and the experience of technicians to identify potential issues. While skilled hands and sharp eyes were essential, this approach left room for human error and was time-intensive.
In the past, maintenance teams would manually inspect aircraft using ladders, scaffolding, and flashlights—documenting findings on paper and scheduling repairs based on fixed timelines rather than actual aircraft performance. While effective for its time, it lacked the precision and predictive capabilities that modern technology offers.
Today, the shift from manual inspection to automated and AI-driven processes has transformed how servicing is done. Advanced sensors, digital tools, and data analytics now allow technicians to detect problems before they occur, minimizing downtime and enhancing safety. Maintenance is no longer purely reactive—it’s predictive, proactive, and data-powered.
Key Technologies in Aircraft Servicing
Technology is now at the heart of aviation maintenance, enabling faster, safer, and more accurate servicing. Here are the most impactful innovations currently shaping the industry:
Predictive Maintenance and Big Data Analytics
Modern aircraft are equipped with thousands of sensors that collect real-time performance data—from engine temperature and vibration patterns to fuel consumption and hydraulic pressure. This constant flow of information is analyzed using big data analytics to detect anomalies or early signs of wear.
-
How it Works: Predictive maintenance uses historical and real-time data to forecast when a component is likely to fail. This allows technicians to schedule repairs before the problem becomes critical.
-
Key Benefits:
-
Prevents in-flight failures.
-
Reduces unexpected downtime.
-
Optimizes maintenance schedules for cost efficiency.
-
For example, if an engine vibration sensor detects unusual patterns, maintenance crews can address the issue during the next ground stop—avoiding costly delays or cancellations.
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS)
CMMS platforms have replaced the paper-based record-keeping systems of the past. These digital tools store detailed information about each aircraft’s maintenance history, service schedules, and parts inventory.
-
Advantages:
-
Centralized access to all maintenance records.
-
Automated reminders for upcoming service tasks.
-
Streamlined compliance reporting for aviation authorities.
-
By integrating CMMS with predictive analytics, airlines can plan maintenance more strategically, ensuring aircraft are serviced at the right time without over-maintaining or risking under-maintenance.
Drone-Assisted Inspections
Inspecting the exterior of a large aircraft can take hours when done manually. Drone technology has revolutionized this process by allowing high-resolution cameras and thermal imaging sensors to quickly scan an aircraft’s fuselage, wings, and tail.
-
Time Savings: What once took up to 6 hours can now be done in less than 30 minutes.
-
Accuracy: Drones can access hard-to-reach areas without scaffolding, reducing the risk to human inspectors.
-
Thermal Imaging: Detects hidden structural damage or insulation failures not visible to the naked eye.
This technology speeds up inspections while improving detection accuracy, reducing turnaround times for aircraft between flights.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR are enhancing both maintenance operations and technician training:
-
AR Glasses: Technicians wearing AR-enabled headsets can see interactive overlays of aircraft parts, access digital manuals, and follow guided repair steps without leaving their work area.
-
VR Training Simulations: Technicians can practice complex repairs or emergency procedures in a virtual environment, reducing errors when working on real aircraft.
This immersive technology reduces training costs, speeds up skill acquisition, and improves repair precision.
3D Printing in Aircraft Parts Replacement
In the past, sourcing replacement aircraft parts could take days or even weeks—especially if parts had to be shipped internationally. 3D printing has drastically cut these delays by allowing maintenance facilities to produce certain components on-site.
-
Benefits:
-
Rapid production of custom or rare parts.
-
Lower storage and shipping costs.
-
Reduced aircraft downtime during repairs.
-
While safety regulations mean that not all critical parts can be 3D-printed yet, the technology is rapidly advancing and is expected to play a major role in future maintenance.
Benefits of Technology in Aircraft Servicing
The integration of modern technology into aircraft servicing has reshaped the aviation industry, offering significant advantages in safety, efficiency, and cost control.
Improved Safety and Accuracy
Technology-driven inspections, such as drone imaging and predictive maintenance, enable earlier detection of mechanical issues. Advanced sensors monitor every critical system in real-time, allowing technicians to identify potential problems before they compromise flight safety. This precision reduces the likelihood of human error and ensures maintenance tasks meet exact specifications.
Reduced Maintenance Time
Automation, drones, and advanced diagnostic tools have shortened inspection and repair times dramatically. Tasks that once required several hours or days can now be completed in a fraction of the time, reducing aircraft downtime and keeping flights on schedule.
Cost Efficiency for Airlines
Predictive maintenance and optimized scheduling help airlines avoid unnecessary repairs and part replacements. Technologies like 3D printing further reduce costs by eliminating expensive supply chain delays. Over time, these savings add up to millions of dollars annually for large fleets.
Better Compliance with Aviation Regulations
Digital record-keeping through Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) ensures that every maintenance action is logged, traceable, and accessible. This makes compliance with FAA, EASA, and other global aviation authorities more efficient and less prone to documentation errors.
Challenges and Limitations
While the benefits of technology in aircraft servicing are substantial, there are still challenges that airlines and maintenance facilities must address.
High Initial Investment Costs
Advanced tools such as AI-powered diagnostic systems, drones, and AR equipment require significant upfront capital. Smaller maintenance providers may find it challenging to adopt these technologies without financial support or phased investment strategies.
Need for Skilled Personnel to Operate New Technologies
Modern maintenance systems require technicians who are not only mechanically skilled but also proficient in digital tools and data analysis. This creates a growing demand for training programs to bridge the skills gap.
Cybersecurity Concerns in Aviation Systems
As aircraft systems and maintenance operations become more connected, they face an increased risk of cyberattacks. Protecting sensitive maintenance data and preventing potential interference with operational systems is a critical priority for the aviation industry.
The Future of Technology in Aircraft Servicing
The pace of technological advancement in aviation maintenance shows no signs of slowing down. In the coming years, we can expect even more sophisticated tools and methods to enhance servicing operations.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial intelligence will play a bigger role in analyzing complex datasets, identifying patterns, and predicting maintenance needs with even greater accuracy. This will allow airlines to further minimize unplanned downtime and extend the life of their fleets.
Fully Automated Servicing Systems
Robotics and automation could take over certain repetitive or hazardous maintenance tasks entirely. From autonomous drones conducting exterior inspections to robotic arms handling component replacements, the future may see a reduced reliance on manual intervention.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Maintenance Practices
Green technologies—such as biodegradable cleaning agents, energy-efficient tools, and waste reduction systems—will become standard in aircraft servicing. Combined with data-driven maintenance, these practices will help airlines meet environmental goals while maintaining operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Technology has revolutionized aircraft servicing, transforming it from a primarily manual process into a data-driven, highly precise, and efficient operation. From predictive maintenance that prevents mechanical failures before they occur, to drone-assisted inspections, AR/VR training, and 3D printing for faster part replacements, each innovation has played a role in making aviation safer, more reliable, and more cost-effective.
FAQs
1. How has technology improved aircraft maintenance?
Technology has introduced tools like predictive maintenance, drones, AR/VR training, and computerized management systems, allowing faster, more accurate inspections and repairs. This reduces downtime, improves safety, and cuts costs for airlines.
2. What is predictive maintenance in aviation?
Predictive maintenance uses real-time sensor data and analytics to forecast when aircraft components will need repair or replacement. This prevents unexpected failures and helps schedule maintenance more efficiently.
3. Why are drones used in aircraft inspections?
Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and thermal imaging can inspect large aircraft in minutes, accessing hard-to-reach areas without scaffolding. This speeds up the process and improves detection accuracy.
4. Can 3D printing be used for aircraft parts?
Yes, 3D printing is increasingly used to produce non-critical and custom aircraft parts on demand. This technology reduces lead times, lowers costs, and minimizes aircraft downtime.
5. What are the main challenges of using technology in aircraft servicing?
The biggest challenges include high initial investment costs, the need for skilled technicians to operate advanced systems, and cybersecurity risks in connected aviation systems.